Understanding AI Learning: The Future of Intelligent Systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) has rapidly transformed from a niche field of study to a cornerstone of modern technology. At the heart of AI’s capabilities is its ability to learn, adapt, and improve over time. This article delves into the various facets of AI learning, exploring how it works and its implications for the future.
What is AI Learning?
AI learning refers to the methods by which machines gain knowledge and skills through experience. It involves algorithms that allow computers to identify patterns, make decisions, and improve tasks without being explicitly programmed for each specific scenario.
Types of AI Learning
- Supervised Learning: In this approach, algorithms are trained on labeled datasets. The system learns to map inputs to outputs based on example input-output pairs.
- Unsupervised Learning: Here, the system is given data without explicit instructions on what to do with it. It must find structure in the data itself, often used for clustering or association tasks.
- Semi-supervised Learning: Combining elements of both supervised and unsupervised learning, this method uses a small amount of labeled data alongside a larger set of unlabeled data to improve learning accuracy.
- Reinforcement Learning: This type involves training models through trial and error. An agent interacts with an environment and learns by receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties.
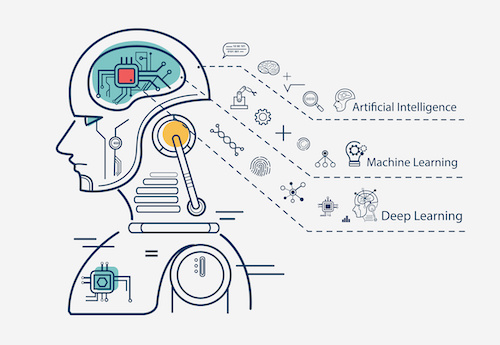
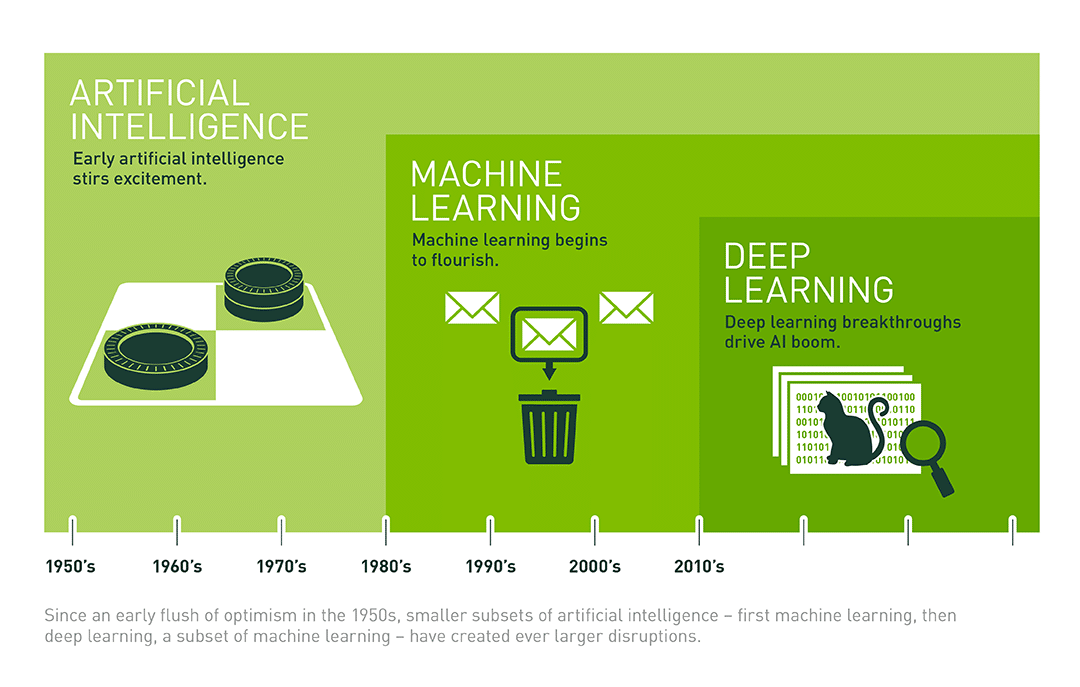
The Role of Neural Networks
A key component in many AI systems is the neural network—an architecture inspired by the human brain. These networks consist of layers of interconnected nodes (or “neurons”) that process information in stages. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning involving neural networks with many layers, has shown remarkable success in fields such as image recognition and natural language processing.
The Impact on Society
The advancements in AI learning have profound implications for various industries. In healthcare, AI systems can assist doctors by analyzing medical images more quickly and accurately than humans alone. In finance, AI algorithms help detect fraudulent transactions by identifying unusual patterns in large datasets.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its potential benefits, AI learning raises several ethical questions. Concerns about privacy arise when systems collect vast amounts of personal data for training purposes. Additionally, there is apprehension about bias in AI models if they are trained on skewed datasets that reflect societal prejudices.
The Future Outlook
The future of AI learning holds exciting possibilities as technology continues to evolve. Researchers are working towards developing more general forms of artificial intelligence that can perform a wide range of tasks across different domains—much like humans do today.
The journey towards smarter machines will undoubtedly transform our world in ways we are only beginning to understand. As we continue down this path, it will be crucial to balance innovation with thoughtful consideration regarding ethical implications and societal impact.
AI learning represents not just a technological advancement but also an opportunity for humanity to redefine what machines can achieve alongside us—heralding an era where intelligent systems enhance our capabilities rather than replace them entirely.
Five Key Advantages of AI Learning: Boosting Efficiency, Accuracy, Personalization, Innovation, and Decision-Making
- 1. Enhances Efficiency
- 2. Improves Accuracy
- 3. Enables Personalization
- 4. Facilitates Innovation
- 5. Enhances Decision-Making
Challenges of AI Learning: Addressing Bias, Transparency, and Job Displacement
1. Enhances Efficiency
AI learning significantly enhances efficiency by automating a wide range of tasks, allowing businesses and individuals to save both time and resources. By taking over repetitive and time-consuming processes, AI systems enable human workers to focus on more strategic and creative endeavors. For instance, in industries like manufacturing, AI can streamline production lines by optimizing scheduling and maintenance routines, reducing downtime. In customer service, AI-driven chatbots handle routine inquiries, freeing up human agents to tackle more complex issues. This automation not only boosts productivity but also reduces operational costs, leading to improved profitability for businesses. As AI continues to evolve, its ability to enhance efficiency will become even more pronounced across various sectors.
2. Improves Accuracy
AI learning significantly improves accuracy by leveraging machine learning algorithms capable of analyzing vast datasets with remarkable precision. Unlike traditional methods, which might struggle with large volumes of data or complex patterns, AI systems can efficiently process and interpret information to identify trends and anomalies. This capability reduces the likelihood of human error in decision-making processes, leading to more reliable outcomes across various fields. For instance, in healthcare, AI can enhance diagnostic accuracy by examining medical images and patient records with greater detail than a human alone could achieve. Similarly, in finance, AI-driven systems can detect fraudulent activities by swiftly identifying irregularities that might be missed by manual review. Overall, the precision of AI learning not only streamlines operations but also ensures higher fidelity in critical decision-making tasks.
3. Enables Personalization
AI learning significantly enhances personalization by analyzing individual preferences and behaviors to tailor experiences uniquely for each user. By leveraging data from past interactions, AI systems can predict what a user might enjoy or need next, whether it’s recommending a new product, curating a playlist, or suggesting personalized content. This level of customization not only improves user engagement but also boosts customer satisfaction by making interactions more relevant and meaningful. As a result, businesses can foster stronger relationships with their customers, leading to increased loyalty and retention. The ability of AI to deliver personalized experiences at scale is transforming industries such as retail, entertainment, and online services, setting new standards for customer interaction.
4. Facilitates Innovation
AI learning plays a pivotal role in facilitating innovation by driving the development of new technologies and solutions that continually push the boundaries of what is possible. Through its ability to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and improve over time, AI learning enables researchers and developers to explore uncharted territories across various fields. This capability not only accelerates the pace of technological advancements but also opens up new avenues for creativity and problem-solving. By leveraging AI learning, industries can devise groundbreaking products and services that address complex challenges, enhance efficiency, and ultimately transform the way we live and work. This constant push towards innovation ensures that AI remains at the forefront of technological progress, offering limitless possibilities for future discoveries.
5. Enhances Decision-Making
AI learning significantly enhances decision-making by equipping organizations with the ability to swiftly analyze vast amounts of data and extract valuable insights. This capability allows businesses to make informed decisions in real-time, leading to more effective strategies and improved outcomes. By identifying patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent to human analysts, AI learning helps companies anticipate market changes, optimize operations, and tailor their products or services to meet customer needs more precisely. As a result, organizations can respond quickly to emerging opportunities and challenges, maintaining a competitive edge in an ever-evolving landscape.
Bias and Discrimination
AI learning, while powerful, is not immune to the biases present in the data it is trained on. When AI systems are developed using datasets that contain historical prejudices or imbalances, they can inadvertently perpetuate these biases in their decision-making processes. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes, particularly in sensitive areas such as hiring, lending, and law enforcement. For instance, if an AI system is trained on data that reflects societal biases against certain groups, it may unfairly disadvantage individuals from those groups when making decisions. This issue underscores the importance of using diverse and representative datasets and implementing rigorous testing to identify and mitigate bias in AI systems. It also highlights the need for ongoing scrutiny and ethical considerations in the development and deployment of AI technologies to ensure fairness and equity.
Lack of Transparency
One significant drawback of AI learning is the lack of transparency inherent in many complex algorithms, often referred to as “black box” models. These systems can process vast amounts of data and make decisions without providing clear insights into their reasoning processes. This opacity poses challenges in terms of accountability, as it becomes difficult for developers and users to trace how specific outcomes are achieved. Consequently, this lack of transparency can erode trust among stakeholders, including businesses, regulators, and the general public. When decisions impact critical areas such as healthcare, finance, or criminal justice, understanding the rationale behind AI-driven conclusions becomes crucial. Without this clarity, it is challenging to ensure fairness and address potential biases within AI systems effectively.
Job Displacement
As AI technology continues to advance, one significant concern is the risk of job displacement due to automation. Many industries are increasingly adopting AI-driven systems to perform tasks that were traditionally carried out by human workers. This shift can lead to significant changes in the job market, with certain roles becoming obsolete as machines prove more efficient and cost-effective. While AI can enhance productivity and drive economic growth, it also poses the threat of unemployment for workers in sectors where tasks are easily automated. The challenge lies in managing this transition by reskilling and upskilling the workforce, ensuring that people can adapt to new roles created by technological innovation while minimizing the negative impact on employment.