Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning: Shaping the Future
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly transformed from a futuristic concept into a tangible reality that is reshaping industries and daily life. At the heart of this transformation lies deep learning, a subset of AI that has enabled machines to perform tasks previously thought to be exclusive to humans.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines designed to think and learn like humans. These systems are capable of performing tasks such as problem-solving, pattern recognition, and decision-making. AI can be categorized into two types:
- Narrow AI: This type is designed for specific tasks, such as facial recognition or language translation.
- General AI: A more advanced form that can understand, learn, and apply knowledge across various domains, similar to human intelligence.
The Role of Deep Learning
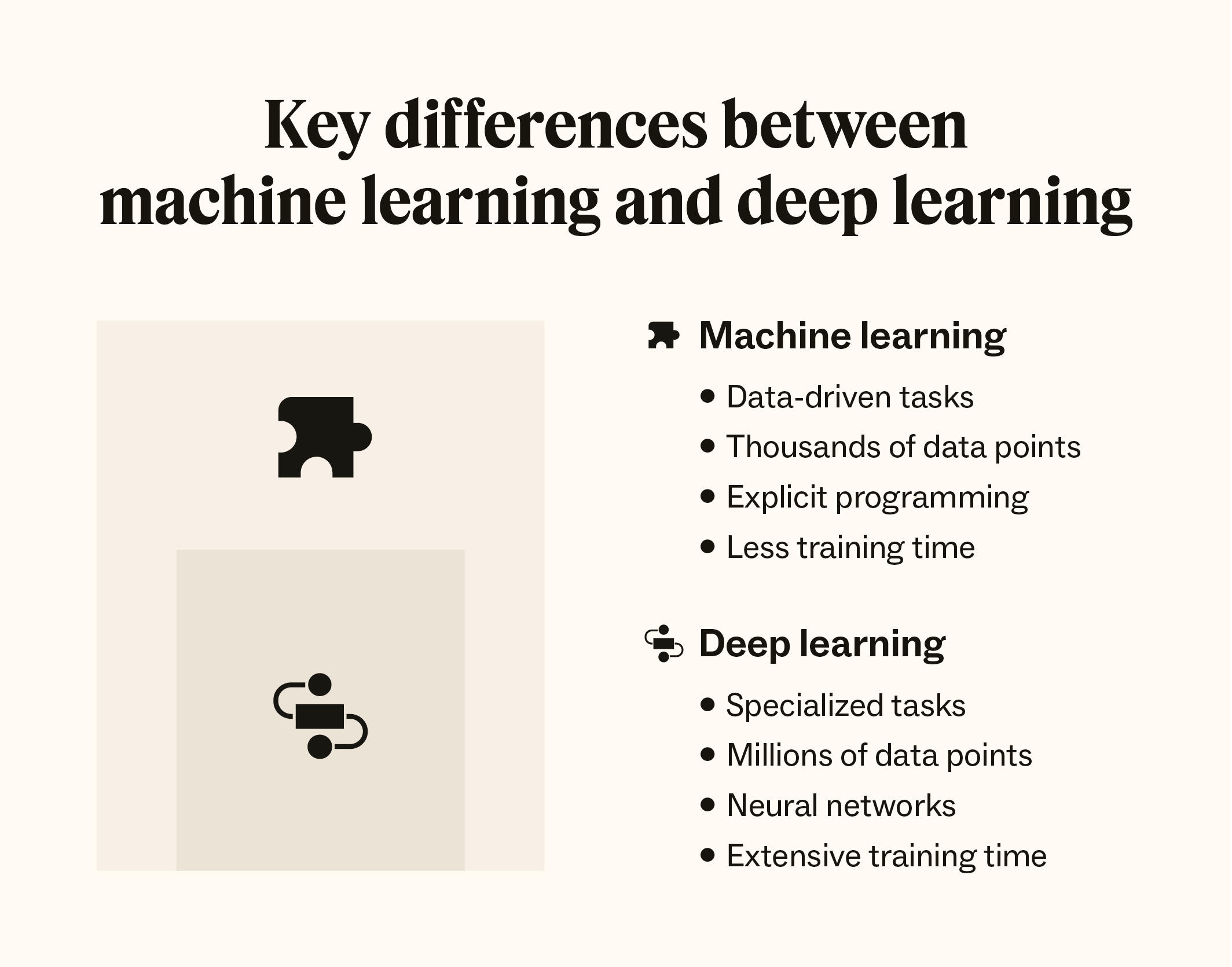
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that utilizes neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) to analyze various factors of data. It mimics the way humans gain certain types of knowledge and is particularly effective in processing large amounts of unstructured data such as images, audio, and text.
How Deep Learning Works
The core component of deep learning is the neural network. These networks consist of layers of nodes or neurons that process input data and generate output. Each layer extracts specific features from the input data before passing it on to subsequent layers for further analysis. This hierarchical approach allows deep learning models to identify intricate patterns within complex datasets.
Applications Across Industries
The impact of AI and deep learning spans numerous sectors:
- Healthcare: AI algorithms assist in diagnosing diseases more accurately by analyzing medical images and patient data.
- Automotive: Self-driving cars rely on deep learning for object detection, path planning, and navigation.
- Finance: Financial institutions use AI for fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and personalized banking services.
- E-commerce: Recommendation engines powered by AI enhance user experience by suggesting products based on consumer behavior.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite its potential benefits, the rise of AI also presents challenges. Ethical considerations such as privacy concerns, bias in decision-making algorithms, and job displacement due to automation must be addressed. Furthermore, ensuring transparency in how these systems make decisions remains a critical issue for developers and policymakers alike.
The Future Outlook
The future of AI and deep learning holds immense promise as technology continues to advance. Innovations in quantum computing could further accelerate progress by providing unprecedented computational power. As researchers strive towards achieving general AI capabilities, society must navigate both opportunities and challenges presented by this transformative technology responsibly.
The journey towards fully realizing the potential of artificial intelligence is ongoing but undeniably exciting—one that promises significant advancements across all facets of life while prompting important discussions about our collective future with intelligent machines at our side.
7 Key Benefits of Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning: Boosting Efficiency, Accuracy, and Innovation
- Enhanced Efficiency
- Improved Decision-Making
- Personalized Experiences
- Increased Accuracy
- Innovative Solutions
- Cost Savings
- Predictive Capabilities
Challenges of AI and Deep Learning: Addressing Bias, Job Displacement, and Privacy Issues
Enhanced Efficiency
Artificial intelligence and deep learning have revolutionized the way businesses operate by significantly enhancing efficiency. By automating repetitive and mundane tasks, these technologies free up valuable time and resources, allowing human workers to focus on more strategic and creative endeavors. For instance, AI algorithms can handle data entry, scheduling, and customer service inquiries with speed and accuracy that surpass human capabilities. This automation not only reduces the potential for human error but also increases productivity across various sectors. As a result, companies can allocate their workforce to tasks that require critical thinking and innovation, ultimately driving growth and improving overall performance.
Improved Decision-Making
Improved Decision-Making is a significant advantage of artificial intelligence and deep learning. By leveraging these technologies to analyze extensive datasets, organizations can gain valuable insights that facilitate more informed and strategic decision-making processes. The ability to extract patterns, trends, and correlations from large volumes of data enables businesses to make well-founded decisions that are based on evidence and analysis, ultimately leading to more effective outcomes and competitive advantages in today’s data-driven landscape.
Personalized Experiences
Artificial intelligence and deep learning have revolutionized the way personalized experiences are delivered across various platforms. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI systems can identify individual preferences and behaviors, allowing for highly tailored recommendations and services. Whether it’s suggesting a new movie based on viewing history, curating a playlist that matches one’s music taste, or offering personalized shopping suggestions, AI enhances user engagement by making interactions more relevant and enjoyable. This level of personalization not only improves customer satisfaction but also fosters brand loyalty as users feel understood and valued. As AI technology continues to evolve, the capacity for delivering even more nuanced and accurate personalized experiences will only increase, further transforming how individuals interact with digital content and services.
Increased Accuracy
Deep learning models excel in identifying patterns and trends within vast datasets, offering a significant advantage in terms of accuracy. These models utilize complex neural networks that mimic the human brain’s processing capabilities, allowing them to analyze data with remarkable precision. This increased accuracy is particularly beneficial in fields such as healthcare, where AI can assist in diagnosing diseases by accurately interpreting medical images and patient records. In finance, deep learning algorithms can predict market trends and detect fraudulent activities with a high degree of reliability. As a result, industries leveraging AI and deep learning can make more informed decisions, reduce errors, and enhance overall efficiency.
Innovative Solutions
Artificial intelligence and deep learning are at the forefront of fostering innovation by opening up new avenues for problem-solving and product development. These technologies enable the creation of innovative solutions that were previously unimaginable, allowing businesses and researchers to tackle complex challenges with unprecedented precision and efficiency. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI systems can identify patterns and insights that humans might overlook, leading to breakthroughs in various fields such as healthcare, where AI assists in developing personalized medicine, or in environmental science, where it helps create sustainable solutions for climate change. Moreover, AI-driven innovation is not limited to existing problems; it also paves the way for entirely new products and services that enhance user experiences and improve quality of life. As a result, businesses leveraging AI are better equipped to stay competitive in an ever-evolving market landscape.
Cost Savings
Implementing artificial intelligence and deep learning systems can significantly contribute to cost savings by optimizing processes and enhancing productivity. By automating routine tasks, AI reduces the need for manual labor, allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities that add greater value. Additionally, AI systems can analyze vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, leading to better decision-making and resource allocation. This efficiency minimizes waste and lowers operational costs. Furthermore, predictive maintenance powered by AI can anticipate equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and repair expenses. Overall, the integration of AI into business operations not only streamlines workflows but also drives substantial financial benefits.
Predictive Capabilities
Deep learning algorithms, a key component of artificial intelligence, possess remarkable predictive capabilities that enable the forecasting of outcomes and trends with exceptional precision. By analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying complex patterns, these algorithms can anticipate future scenarios across various domains, from financial markets to healthcare diagnostics. This predictive power not only enhances decision-making processes but also empowers organizations to proactively address challenges and seize opportunities before they unfold.
Bias and Discrimination
AI algorithms, particularly those powered by deep learning, can inadvertently perpetuate and even amplify biases present in the data used for their training. This occurs because these systems learn patterns and make decisions based on historical data, which may contain prejudices or reflect societal inequalities. As a result, AI can produce discriminatory outcomes in critical areas such as hiring, law enforcement, and lending. For instance, if an AI system is trained on biased datasets that underrepresent certain groups or reflect existing stereotypes, it may unfairly disadvantage these groups in its decision-making processes. Addressing this issue requires careful consideration of data sources and the implementation of strategies to identify and mitigate biases before they affect real-world applications.
Job Displacement
The rapid advancement of AI and deep learning technologies has led to significant automation across various industries, resulting in concerns about job displacement. As machines and algorithms become increasingly capable of performing tasks traditionally carried out by humans, there is a growing fear that many jobs could become obsolete. This shift is particularly evident in sectors such as manufacturing, transportation, and even customer service, where routine and repetitive tasks are easily automated. The potential for widespread unemployment poses a serious challenge, as workers may find themselves needing to acquire new skills or transition into entirely different fields to remain competitive in the job market. Addressing this issue requires proactive measures, including investing in education and retraining programs to equip the workforce with the necessary skills for emerging roles in an AI-driven economy.
Privacy Concerns
The widespread adoption of artificial intelligence and deep learning technologies has brought privacy concerns to the forefront, as these systems often rely on extensive data collection and analysis. AI applications in various sectors gather vast amounts of personal information to enhance their performance and accuracy. However, this raises significant issues regarding the security and confidentiality of sensitive data. The potential for unauthorized access, data breaches, and misuse of personal information poses a threat to individual privacy rights. As AI systems become more integrated into daily life, ensuring robust data protection measures and transparent practices is crucial to maintaining public trust and safeguarding personal privacy.